Introduction: Ghost vs WordPress in 2025 - quick answer first
If you want maximum control and infinite flexibility, choose WordPress. If you want a focused, fast publishing workflow with built‑in memberships and newsletters, choose Ghost. In short: WordPress is the Swiss‑army CMS that can do almost anything; Ghost is the streamlined publishing engine built to help you ship content and monetize quickly. Your best pick depends on your content strategy, team resources, and growth plan.
Who this guide is for:
Solo creators and newsletter publishers who value speed and simplicity
SaaS/startups that need SEO-friendly, low-maintenance blog infrastructure
Content teams that require extensibility, workflows, and deep customization
Brief note: If you want a done‑for‑you, AI-powered blog that launches in minutes, consider BlogBowl - an alternative we’ll mention later that automates content, SEO, and publishing so you can focus on growth. Visit https://www.blogbowl.io
"WordPress powers ~43% of websites using a known CMS." - Source
Comparison at a glance (skim-friendly)
Factor | WordPress | Ghost |
|---|---|---|
Hosting model | Self-hosted (flexible) or hosted plans | Ghost(Pro) hosted; self-hosting via Node.js possible |
Learning curve | Moderate to steep (many settings/plugins) | Easy (minimal, writing-first) |
Customization | Massive themes/plugins ecosystem; full-code control | Limited themes; lighter customization |
Monetization approach | Plugins for memberships, ecommerce, courses | Built-in memberships, paywalls, newsletters |
SEO setup | Powerful via plugins + fine-grained control | Strong defaults built-in; minimal setup |
Performance | Varies by host/theme/plugins; needs tuning | Fast by default; lightweight stack |
Typical monthly cost | Hosting $5–$30+ (plugins may add) | Subscription for Ghost(Pro); self-host VPS $5–$15+ |
What you’ll learn in this guide
How each platform impacts cost, time-to-launch, SEO, speed, and long-term maintenance
When Ghost wins, when WordPress wins, and when a simpler alternative makes sense
Pricing and TCO: what you’ll really pay over 12–24 months
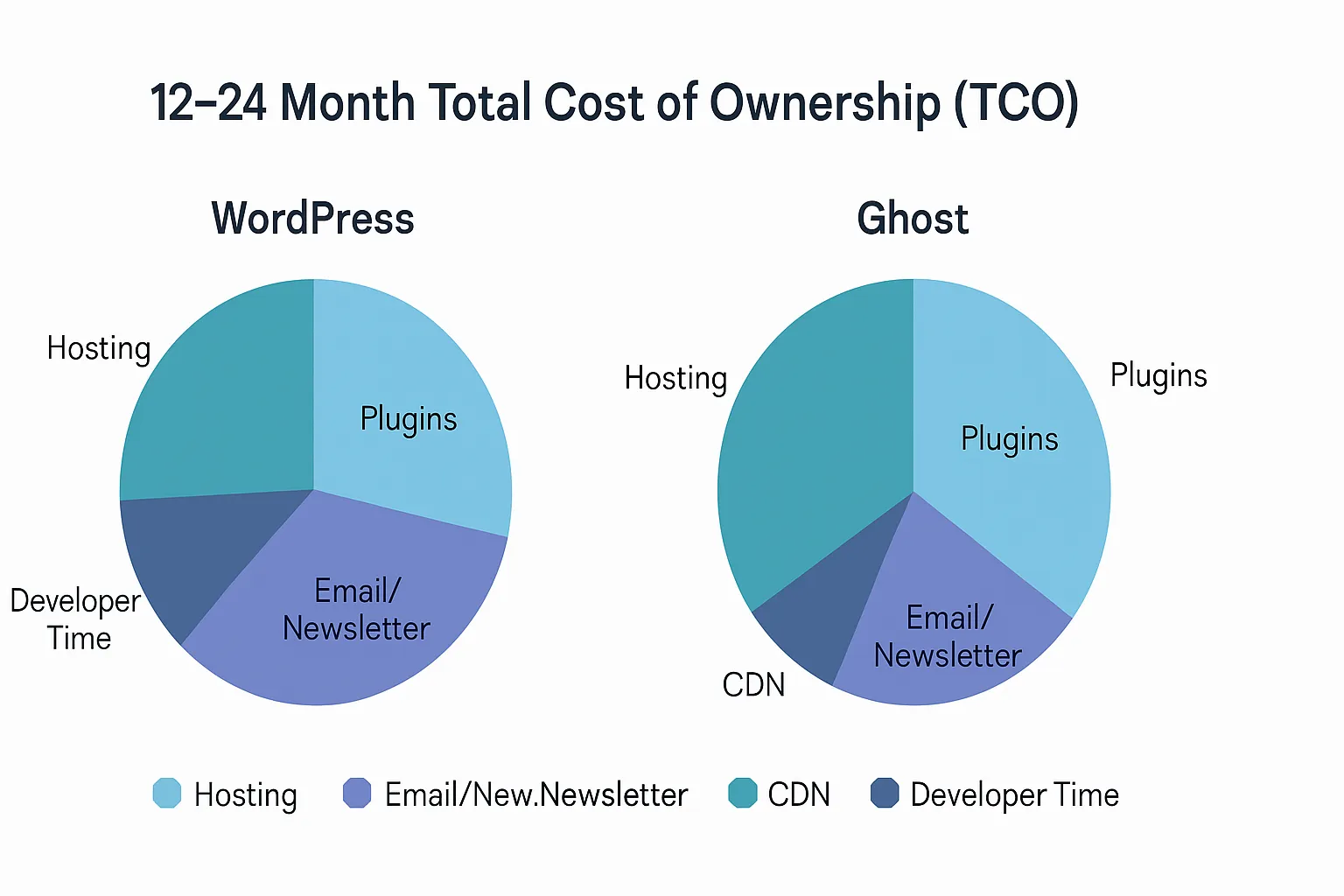
WordPress
Core software is free; costs come from hosting (shared vs managed), premium themes, plugins (SEO, backup, security, performance), newsletter/email tools, CDN, and developer time.
Typical scenarios with sample monthly ranges:
Starter blog: $8–$35 (basic hosting, free theme, 1–2 essential plugins, low-volume email).
Growth-stage content site: $60–$250+ (managed hosting/CDN, premium theme, multiple premium plugins, dedicated email tool, occasional dev hours).
Ghost
Ghost(Pro) plan tiers based on member counts with email volume included; fewer add-ons needed (SEO, newsletter, memberships are built in).
Predictable spend vs usage-based growth (members/subscribers). Self-hosting can reduce software costs but adds server management time.
Break-even analysis & hidden costs
When Ghost is cheaper: you’d otherwise buy multiple premium plugins (SEO, cache/performance, security, membership/paywall) plus a separate newsletter ESP.
When WordPress is cheaper: tight budget, DIY shared hosting, minimal premium stack, and willingness to manage updates/security.
Time cost: WordPress maintenance (updates, conflicts, backups, performance tuning) vs Ghost’s “set-and-forget” simplicity.
Practical advice
Budget templates for your first year:
WordPress starter: $150–$400; growth: $900–$3,000+ (plugins, email, upgrades, occasional dev).
Ghost(Pro): aligned to member tiers; add buffer for growth in subscribers.
How to avoid lock-in and overbuying: start lean (free themes, essential plugins), use portable formats (Markdown/CSV exports), and upgrade plans only when metrics justify the spend.
Scenario | WordPress Estimated Monthly | Ghost Estimated Monthly | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Solo starter blog | $8–$35 | Tier for low members | WP cheapest if you DIY and keep plugins minimal |
Newsletter-led blog | $40–$120 | Comparable or lower | Ghost wins if replacing ESP + memberships |
Growth-stage content site | $60–$250+ | Mid–higher tier | WP scales with managed hosting + plugins; Ghost scales with members |
In-house dev unavailable | +$0–$300 (ad hoc) | Minimal | Ghost reduces maintenance overhead |
Self-hosting option | $5–$25 VPS + time | $5–$25 VPS + Node | Both can be self-hosted; Ghost simpler stack for publishing features built-in |
Setup and Learning Curve: time-to-first-publish
WordPress
Setup paths: WordPress.com vs self-hosted (.org)
WordPress.com: hosted, fastest to start; you’ll pick a theme and publish right away.
Self-hosted WordPress.org: choose a host, connect a domain, then install WP.
1‑click installers: common with most hosts; reduce setup to minutes.
Manual install: upload files, create database, run installer; more control, more steps.
Onboarding complexity (themes, settings, plugins)
Themes: picking, configuring headers/footers, menus, and typography can take longer than expected.
Settings: permalinks, comments, media, and reading settings need a pass before launch.
Plugins: selecting essentials (SEO, caching, security, backups, forms, newsletter) introduces decisions and potential overlaps.
Maintenance overhead
Updates: core, theme, and plugin updates are frequent; schedule a weekly or bi‑weekly maintenance window.
Conflicts: plugin/theme incompatibilities happen - test updates on staging if possible.
Housekeeping: backups, spam prevention, image optimization, and performance tuning add ongoing workload.
Ghost
Ghost(Pro) onboarding speed; streamlined admin; minimal knobs
Sign up, pick a theme, set branding and navigation, import subscribers (optional), publish. SEO, memberships, and newsletters are built in - no plugin hunt.
Editor and settings are minimal and clean, optimized for writing and paywalled content.
Where complexity can show up
Custom themes: Handlebars-based themes and advanced routing add dev time.
Self-hosting Ghost: requires server access, CLI setup, reverse proxy/SSL, and routine patching - best for technical teams.
Migration & launch timeline
Typical hours/days to first article live
WordPress.com: 30–90 minutes (theme selection + basic settings).
WordPress.org (1‑click): 1–3 hours (DNS, theme setup, essential plugins).
WordPress.org (manual): 3–6 hours+ (server + DB setup, then theme/plugins).
Ghost(Pro): 15–45 minutes (theme, brand, first post; newsletter optional).
Self-hosted Ghost: 2–4 hours+ (server provisioning, install, SSL, theme).
How to prototype quickly
WordPress: use a lightweight default theme, publish a “Hello World” post, defer heavy plugin stack; add a simple menu and essentials only.
Ghost: launch with the default theme, publish your first post, enable free memberships later; keep code injection/custom routes for phase two.
No‑code helpers: build draft outlines in docs, import/export Markdown, and use simple design presets before custom styling.
Governance basics (roles, permissions) for teams
WordPress: use core roles (Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor) to separate publishing from admin tasks; limit plugin access to admins.
Ghost: Owner/Admin for settings, Editor for content oversight, Authors for writing, Contributors for drafts; enable review workflows via roles.
Writing Experience and Workflow: where you spend your day
WordPress
Block Editor (Gutenberg) overview; strengths and quirks
Gutenberg’s block-based editor enables rich layouts with reusable patterns, columns, calls-to-action, tables, and more. Strengths: design freedom, media embeds, and a growing library of native blocks and third‑party block packs. Quirks: occasional block nesting confusion, styling inconsistencies across themes, and reliance on theme compatibility for pixel‑perfect output.
Content modeling: posts, pages, categories/tags, custom post types
Out of the box, you’ll use Posts (chronological content) and Pages (static), organized with Categories and Tags. For advanced needs - like case studies, changelogs, or docs - register Custom Post Types and custom taxonomies for structured, scalable content models.
Collaboration, revisions, editorial calendar (plugins)
Native revisions, draft autosave, and role-based permissions support teamwork. For editorial calendars, task assignments, content statuses, and checklists, install specialized editorial workflow plugins to streamline planning and approvals.
Ghost
Distraction-free editor; built-in newsletter sending
A clean, minimal editor focused on writing speed and readability. Publish to the web and send newsletters from the same draft, eliminating copy/paste into external ESPs.
Posts/pages and tags; simple content model that stays out of the way
Ghost keeps it lean: Posts and Pages with Tags for organization. Less to configure means faster publishing and fewer edge cases to maintain.
Built-in memberships gating; publish once to web + inbox
Gate sections or full posts for members (free/paid) without extra tools. Publish once and deliver to both your site and subscribers - ideal for content-led monetization.
Productivity features to check
Keyboard shortcuts, slash commands, embeds, media handling
Speed up drafting with keyboard shortcuts and “/” commands to insert blocks (images, quotes, callouts, tables, buttons). Both platforms support rich embeds (YouTube, tweets, code snippets) and responsive images, though WordPress gains extra block types via plugins/themes.
Drafting → review → schedule → update flow
Draft, add internal notes, request review, then schedule by timezone. WordPress often relies on workflow plugins for granular statuses and checklists; Ghost favors a simpler, writer-first flow with frictionless scheduling and member targeting.
Content reuse (templates, patterns, snippets)
WordPress: block patterns, synced patterns, reusable blocks, and template parts for consistent page sections. Ghost: theme-level partials and simple post templates; leaner but fast for repeat formats like newsletters or briefs.
Design, Customization, and Integrations
WordPress
Theme ecosystem scale; site editor; child themes
Thousands of free and premium themes, plus modern Block Themes that work with the Site Editor for full‑site design control. Child themes let you safely override styles and templates without losing changes on updates.
Plugin ecosystem breadth (forms, SEO, ecommerce, caching, LMS, communities)
An unmatched library spans forms, SEO, performance/caching, accessibility, ecommerce, learning management, forums/communities, multilingual, and more - ideal if you need specialized features or complex workflows.
Custom code options, REST API/GraphQL via plugins, headless setups
Deep extensibility with custom PHP/JS, hooks, and the REST API. Add GraphQL via plugins, or run headless architectures with front ends like Next.js/Gatsby for performance and multichannel content delivery.
Ghost
Minimal theme marketplace; Handlebars-based themes
A smaller marketplace with clean, content‑first designs. Themes are built with Handlebars templates, CSS, and partials - great for lean, fast sites with consistent typography and reading UX.
Integrations via native features, webhooks, and Zapier/Make
Core publishing, SEO, memberships, and newsletters are built in; extend with webhooks and automation platforms to connect CRMs, payments, or analytics with minimal overhead.
Custom code via theme development; content-first layouts
Customize layouts and components at the theme level; prioritize readability, speed, and simplified structure over heavy design frameworks.
What to consider
Time-to-unique design vs effort/complexity
WordPress can achieve a pixel‑perfect, brand‑specific look quickly with a premium theme and Site Editor, but deep customization adds complexity. Ghost ships fast with elegant defaults; bespoke visuals require more theme work.
Risk of bloat vs stability and speed
WordPress flexibility can introduce bloat (multiple plugins, heavy themes). Vet every plugin and use performance best practices. Ghost’s lean stack minimizes moving parts, helping maintain consistent speed and fewer conflicts.
Vendor viability and support for critical plugins
In WordPress, ensure long‑term plugin/theme support, update cadence, and clear roadmaps for mission‑critical features. With Ghost, confirm ongoing theme maintenance and review integration options for must‑have workflows.
SEO and Performance
WordPress
SEO via plugins (Yoast, Rank Math): detailed control over titles, schema, redirects
Granular per‑post metadata, auto‑generated sitemaps, advanced schema types, and redirect management give power users full control of on‑page SEO.
Performance depends on stack: theme quality, caching/CDN, image optimization
Lightweight themes, server‑level caching, a global CDN, and modern image formats (WebP/AVIF) are key to fast renders.
Core Web Vitals tuning is possible but requires configuration
Optimize LCP/CLS/INP with lazy loading, critical CSS, preloading key assets, and minimizing plugin bloat; staging tests are recommended before rollout.
Ghost
SEO features built in (sitemaps, structured data, canonical tags)
Strong defaults out of the box; fewer knobs to misconfigure and no plugin sprawl for basics.
Lightweight stack with strong defaults; excellent out-of-the-box speed
Minimal theme overhead and efficient rendering support fast TTFB and good CWV without heavy tuning.
Newsletter + web helps diversify traffic beyond search
Publish once to web and inbox to reduce reliance on SERPs and sustain engagement during algorithm shifts.
"Independent tests have shown Ghost to be up to ~1,900% faster than WordPress (request handling)." - Source
Bottom line
Choose control (WordPress) vs strong defaults (Ghost) based on your skills and time
If you enjoy fine‑tuning SEO and performance stacks, WordPress gives unmatched control. If you prefer speed without setup, Ghost’s defaults are compelling.
How both can meet CWV thresholds with the right setup
WordPress: pair a lightweight theme with server caching, CDN, and disciplined plugin choices. Ghost: select a lean theme, enable CDN, and keep custom scripts minimal.
Monetization and Audience Growth
WordPress
Ecommerce (WooCommerce), paywalls/memberships (MemberPress, etc.)
Full storefronts, product bundles, and checkout customization; memberships and paywalls via dedicated plugins; course delivery with LMS extensions.
Newsletters via ESP integrations (Mailchimp, ConvertKit, etc.)
Use forms and automations to capture subscribers, segment audiences, and trigger multi‑step sequences; embed signup blocks across posts and pages.
Advanced funnels possible - more setup, more moving parts
Combine analytics, CRM, A/B testing, retargeting, and personalization; expect higher complexity and maintenance.
Ghost
Native memberships, paid tiers, and newsletter delivery built in
Gate content by member tier, bill subscribers, and publish once to web + inbox with minimal configuration.
Audience dashboard (segments, member profiles)
View engagement, cohorts, and member activity; send targeted posts and emails to segments.
Referral programs/integrations to accelerate growth
Leverage native features and automation platforms to power referrals, perks, and lifecycle nudges.
Strategic guidance
When to monetize with memberships vs products/courses
Memberships fit recurring insights, analysis, and community value. Products/courses suit finite transformations and packaged expertise.
Reducing tool sprawl vs maximizing customization
Ghost reduces moving parts for membership-led media. WordPress maximizes flexibility for multi-offer stacks (courses, shops, communities).
Data ownership, deliverability, and churn considerations
Keep exports portable (members/subscribers, orders). Prioritize reliable email deliverability and set clear win‑back and downgrade paths to manage churn.

Security, Maintenance, and Hosting Options
WordPress
Security posture: the importance of updates, reputable plugins, WAF/CDN
Keep core, themes, and plugins patched on a regular cadence (weekly or faster for critical releases). Use only reputable plugins with active maintenance and minimize the total count to reduce attack surface.
Add a Web Application Firewall (WAF) and a global CDN to mitigate DDoS, block common exploits, and accelerate delivery. Enforce strong auth (2FA), least‑privilege roles, and automatic brute‑force protection.
Backups, staging, and monitoring (managed hosts simplify)
Automate off‑site backups (daily or more) and test restores quarterly. Use a staging site for updates and theme changes to avoid production downtime.
Monitor uptime, SSL renewals, and error logs; configure alerting for performance anomalies and failed cron tasks.
Shared vs VPS vs managed WordPress hosting: trade-offs
Shared hosting: cheapest, but noisy neighbors and limited resources; fine for small blogs with light traffic.
VPS: more control and scalability; you are responsible for server hardening, updates, and stack tuning.
Managed WordPress: higher cost, lowest operational burden (automatic updates, backups, staging, security hardening), ideal as you scale.
Ghost
Ghost(Pro) handles updates, security, and performance at the platform level
Managed hosting includes core updates, security patches, CDN, and performance tuning - reducing operational overhead for content teams.
Self-hosting Ghost (Node.js) requires CLI familiarity
Install via CLI, configure reverse proxy/SSL, and maintain system packages. Plan for regular upgrades and monitor memory/CPU for spikes.
Backup/restore and uptime considerations
Ensure scheduled database exports and theme backups; validate restores on a secondary instance. Use status monitoring and alerting for uptime and mail delivery.
Risk management
Minimizing attack surface (plugin discipline vs baked-in features)
WordPress: adopt a “less is more” plugin policy; remove unused themes/plugins and lock admin endpoints. Ghost: benefit from fewer moving parts and more built‑in capabilities, reducing third‑party risk.
Compliance and privacy basics (consent, data retention)
Implement consent banners, data‑retention policies, and clear unsubscribe flows. Limit PII collection, encrypt data in transit, and document vendor DPAs for ESPs and analytics.
Operational runbooks for small teams
Define owners for patches, backups, and incidents; create a monthly maintenance checklist; keep a change log and rollback plan; run tabletop drills for content restore and email deliverability issues.
Scalability, Teams, and Ecosystem Support
WordPress
Scales from small blogs to enterprise with proper hosting and caching
With a solid stack (object/page caching, CDN, database optimization), WordPress can handle high-traffic spikes, complex content models, and large media libraries. Edge caching and optimized query patterns are essential for scale.
Multi-site options; granular roles/capabilities
WordPress Multisite enables networked properties (e.g., regional blogs, product lines) under one install. Fine‑grained roles/capabilities and custom user permissions support editorial governance and compliance.
Massive community, agencies, and documentation; paid support via hosts
A huge ecosystem of agencies, freelancers, and solution providers reduces vendor risk. Extensive documentation and forums help DIY teams; managed hosts offer SLAs, staging, and support escalation as you grow.
Ghost
Scales well on Ghost(Pro); member-count based tiers
Ghost(Pro) abstracts the infrastructure, CDN, and updates, letting you scale member growth and email volume without re-architecting. Tiers align spend with audience size.
Roles/permissions for publications; simpler governance model
Clear roles (Owner/Admin, Editor, Author, Contributor) suit lean content teams. Governance is simpler than WordPress, making it easier to maintain editorial discipline without heavy config.
Smaller ecosystem but focused docs and direct platform support
While third‑party options are fewer, official docs and direct support shorten troubleshooting cycles - especially valuable for membership‑led publications.
Choosing support models
DIY + community vs vendor SLAs
WordPress: best for teams comfortable owning the stack (plugins, performance, security) or those partnering with a managed host/agency for SLAs and round‑the‑clock coverage.
Ghost: ideal if you want vendor‑managed updates, predictable performance, and direct platform support with minimal operational overhead.
Estimating future needs (traffic, contributors, members)
Project 12–24 months of growth: anticipated traffic peaks, contributor/editor headcount, and member/subscriber milestones. Choose a platform whose governance, pricing tiers, and support options won’t force a migration at your next inflection point.
Final Verdict: quick decision paths
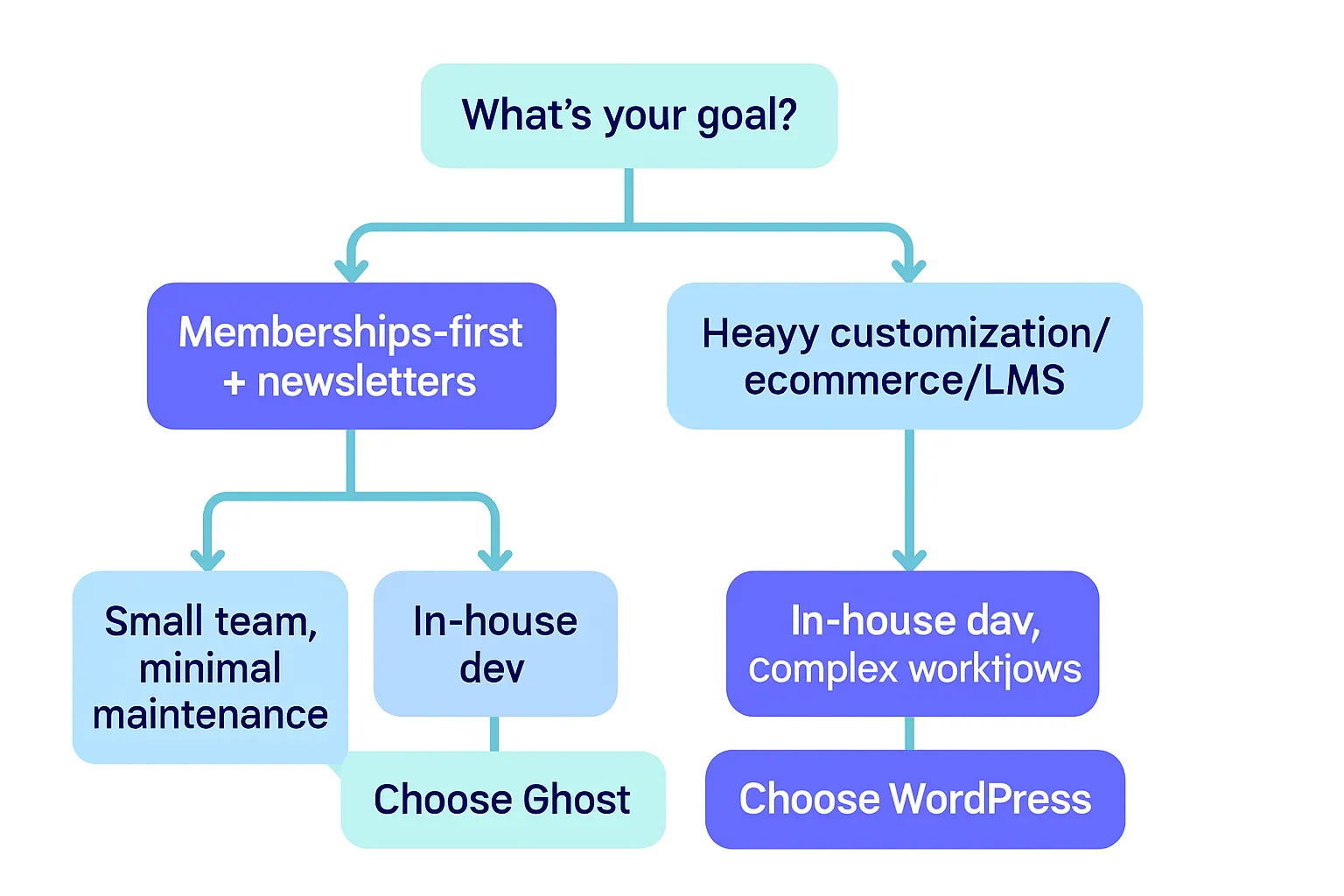
Choose Ghost if…
You want the fastest route to a clean, fast, membership-ready publication
You value built-in newsletters/memberships and minimal maintenance
You prefer opinionated simplicity over infinite extensibility
Choose WordPress if…
You need maximum flexibility (complex site structure, ecommerce, custom features)
You want to own every layer (hosting, plugins) and have time/skills to manage
You plan to extend into LMS/communities or complex editorial workflows
Decision checklist
Content model, monetization plan, SEO control needs, performance expectations, budget, team skills, launch deadline
Considering an even simpler route: BlogBowl
Launch a fast, SEO-optimized blog in under 60 seconds
AI-automates daily articles, internal linking, keyword research, images/video embeds
Built-in newsletter, analytics, unlimited blogs/docs, no-code customization
Ideal for SaaS/startups that want traffic growth on autopilot without managing stacks
Next steps
Try a low-stakes pilot on each for a week
Validate TCO and content workflow with 3–5 real posts
Reassess against the checklist


