Why meta tags and technical SEO still matter in 2025
Your best content can underperform if search engines can’t read, interpret, and present it correctly. In 2025, blog meta tags and technical SEO are still the levers that influence how Google and AI assistants discover, rank, and display your posts - especially title links, snippets, canonicalization, indexability, and structured data. Clean signals mean better eligibility, richer results, and higher click-through rates.
"Sites that follow the Search Essentials are more likely to show up in Google's search results." - Source
What you’ll learn in this checklist (titles, descriptions, canonicals, robots, schema, sitemaps)
Titles that rank and get clicks: how to write title tags that align with intent and avoid truncation
Meta descriptions that boost CTR without keyword stuffing
Canonical tags to consolidate duplicate URLs and protect rankings
Robots directives (meta robots and robots.txt) to control crawling and indexing safely
Core schema for blogs (Organization, WebSite, Article, Breadcrumb) to unlock rich results
Sitemaps (XML + image/video where relevant) and how to submit/monitor in Search Console
Platform-by-platform steps for WordPress, Blogger (Blogspot), and Google Sites
Quick QA checks to catch indexability and snippet issues before they cost you traffic
Who this is for: WordPress, Blogger (Blogspot), and Google Sites users
WordPress: You want a practical, low-friction “seo for blog posts” workflow using reliable plugins and lightweight themes, without turning your site into a maintenance project.
Blogger (Blogspot): You need “seo for blogger blogspot” basics - clean titles, descriptions, and index controls - with workarounds where the platform is limited.
Google Sites: You want a simple path to indexable pages, solid titles/descriptions, and a sitemap submission routine even with fewer customization options.
Teams using BlogBowl or similar tools: You want blog content SEO handled automatically - titles, schema, sitemaps, and internal linking - so you can focus on writing.
The 80/20 of blog meta tags: what moves rankings and clicks
Title tag = primary ranking and CTR lever
Front-load primary intent; keep it clear, unique, and under ~60 characters where possible.
Meta description = CTR nudge
Summarize benefit + key terms naturally; aim for ~150–160 characters. Not a ranking factor - but a proven click driver.
Canonical tag = authority consolidation
Prevent duplicate URLs (UTM variations, category/tag archives) from splitting signals. Canonicals help Google focus on the right URL.
Robots controls = indexability insurance
Use meta robots (index, follow) prudently; avoid accidental noindex on live posts. Keep robots.txt lean - don’t block CSS/JS needed for rendering.
Schema (Article, Organization, WebSite, Breadcrumb) = eligibility for richer search display
Helps Google understand entities and page type, improving how your “google blog writing” appears in SERPs.
Sitemaps = faster discovery and debugging
Clean, auto-updating XML sitemaps make it easier for Google to find fresh posts and for you to catch coverage issues in Search Console.
These elements are the backbone of a “best SEO blog” setup: they influence what gets indexed, which URL ranks, and how your snippet earns the click.
How to use this guide: skim first, then complete your platform’s section and the final QA
Skim the whole checklist first
Get familiar with the essentials - titles, descriptions, canonicals, robots, schema, sitemaps - and why each matters to blog content SEO.
Complete your platform’s steps
WordPress: Configure your SEO plugin, theme settings, and schema. Validate titles, canonicals, and sitemaps.
Blogger (Blogspot): Set custom title/description, ensure clean permalinks, and control indexability.
Google Sites: Confirm page titles/descriptions, connect a custom domain if possible, and submit the sitemap through Search Console.
Run the final QA pass on every post
Title present, unique, and intent-matched
Meta description concise and compelling
Canonical points to the preferred URL
Page is indexable (no accidental noindex; not blocked by robots.txt)
Article/Breadcrumb schema valid
Included in XML sitemap and submitted to Search Console
Optional: Automate with BlogBowl
BlogBowl can auto-generate SEO-friendly titles, descriptions, schema, sitemaps, and internal links - ideal if you want “google article writing” consistency at scale without manual overhead.
The essential blog meta tags (with templates that boost CTR)
Meta tags are the “visible handshake” between your content and searchers. Done right, they lift click-through rates and help search engines choose the right URL, snippet, and social card. Below is the practical 80/20 for blog content SEO - what to write, where to place it, and how to validate it fast.
Title tags: character and pixel limits, intent-first phrasing, keyword placement
Your title tag is the single biggest on-page lever for both rankings and clicks. Lead with intent, keep it unique per post, and avoid truncation.
Intent-first phrasing: Put the core query up front and promise a clear outcome or benefit.
Natural keyword placement: Include the primary keyword early without stuffing.
Avoid boilerplate: Keep site name for the end - or omit it on ultra-tight titles.
Tip:
Aim for ≈55–60 characters. On desktop, titles truncate near 580–600 px. Longer titles may still work if important words are front-loaded.
"The highest conversion rates occur on pages loading between 0–2 seconds; conversion rate declines with each additional second." - Source
Why it matters here: fast pages show more of your title and snippet sooner, reduce pogo-sticking, and support higher CTR from SERPs.
Meta descriptions: promise + benefit + CTA; when Google rewrites them
Descriptions aren’t a ranking factor, but they strongly influence clicks. Write them for humans - promise value, highlight a benefit, and end with a micro-CTA.
Formula: Promise + Key benefit + Specific outcome + CTA (e.g., “compare, download, learn in minutes”).
When Google rewrites: If your description is missing, duplicated, too long, or mismatched with a query, Google may pull a dynamic snippet from the page. That’s okay - your job is to provide a concise default that sells the click.
Tip:
Aim for ≈150–160 characters. Desktop snippets often truncate around 920–980 px. Put the strongest value first.
Robots meta: index/noindex, follow/nofollow, max-image-preview, and when to use them
Robots directives control indexing and link discovery. Use them to prevent thin or duplicate pages from entering the index and to enable richer previews.
index/noindex: Use noindex on thin archives, test pages, and tag pages you don’t want ranking.
follow/nofollow: Use follow by default; nofollow for untrusted or user-generated outbound links (or annotate per-link).
max-image-preview: Use max-image-preview: large to enable richer image snippets where eligible.
Tip:
Don’t block CSS/JS in robots.txt - Google needs them to render your page accurately.
Canonical tags: consolidating duplicates and parameters (UTM, session IDs)
Canonicals help search engines pick the one URL to rank when duplicates exist (e.g., tracking parameters, paginated views, or near-duplicates).
Self-canonical on primary posts.
Point variants (e.g., ?utm_source, session IDs) to the clean URL.
Avoid conflicting signals: Don’t pair rel=canonical to A while redirecting to B.
Tip:
If two pages truly serve the same intent, canonicalize the weaker one to the stronger, then add internal links to reinforce the preferred URL.
Social cards: Open Graph and Twitter tags to improve shares and secondary traffic
Open Graph (Facebook/LinkedIn) and Twitter Card tags control how your post looks when shared - title, description, and image. Strong social cards earn more clicks from shares, newsletters, and messaging apps.
og:title, og:description, og:url, og:image
twitter:card (summary_large_image), twitter:title, twitter:description, twitter:image
Use a 1200×630 image (or platform-recommended) with crisp text and brand cues.
Tip:
Keep OG/Twitter titles aligned to your HTML title but not necessarily identical - social readers respond well to benefit-led phrasing.
Copy/paste templates by platform (WordPress, Blogger, Google Sites)
Use these reusable snippets and patterns to move fast without sacrificing quality.
# WORDPRESS (Yoast SEO / Rank Math) TITLE & DESCRIPTION TEMPLATES # Yoast SEO
Title template: %%title%% | %%sitename%%
Meta description: %%excerpt%% # Rank Math
Title template: %title% %sep% %sitename%
Meta description: %excerpt% # Notes:
# - Let the plugin output canonical and robots automatically for posts.
# - Override per-post when needed (e.g., noindex on thin archives).
<!-- BLOGGER (BLOGSPOT) - Add to Theme > Edit HTML in <head> -->
<b:if cond='data:blog.pageType == "item"'> <title><data:blog.pageName/> | <data:blog.title/></title> <meta name="description" expr:content='data:post.snippet'/> <link rel="canonical" expr:href='data:blog.canonicalUrl'/> <meta name="robots" content="index, follow, max-image-preview:large"/> <!-- Open Graph --> <meta property="og:type" content="article"/> <meta property="og:title" expr:content='data:blog.pageName " | " + data:blog.title'/> <meta property="og:description" expr:content='data:post.snippet'/> <meta property="og:url" expr:content='data:blog.canonicalUrl'/> <meta property="og:image" expr:content='data:post.firstImageUrl'/> <!-- Twitter --> <meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image"/> <meta name="twitter:title" expr:content='data:blog.pageName " | " + data:blog.title'/> <meta name="twitter:description" expr:content='data:post.snippet'/> <meta name="twitter:image" expr:content='data:post.firstImageUrl'/>
</b:if>
# GOOGLE SITES (WORKFLOW)
# - Set Page title and Description in Pages > Properties.
# - Use a custom domain for clean canonicals.
# - Submit the Sites-generated sitemap in Google Search Console.
# - For social cards, ensure a high-quality featured image is present on the page.
Preview & validate: SERP snippet tools and social share debuggers
Before you publish, preview how your post will appear - both in Google and across social networks.
SERP previews:
Use your SEO plugin’s snippet editor (Yoast/Rank Math) to check length, truncation, and mobile/desktop variants.
Confirm primary keyword visibility in the first ~50–55 characters.
Social debuggers:
Facebook Sharing Debugger and LinkedIn Post Inspector refresh cached OG data.
X/Twitter Card Validator validates summary_large_image rendering.
Technical checks:
View source to confirm one canonical per page and a single, consistent robots meta tag.
Ensure OG and Twitter tags reference an absolute URL for images (HTTPS, publicly accessible).
How BlogBowl helps:
BlogBowl auto-generates SEO-friendly titles, meta descriptions, canonicals, robots, and OG/Twitter tags for every post. You can override per article, but the defaults are tuned for “blog meta tags” best practices - ideal for fast, consistent “seo for blog posts” on WordPress, Blogger (Blogspot), and Google Sites.
WordPress: step-by-step technical SEO checklist
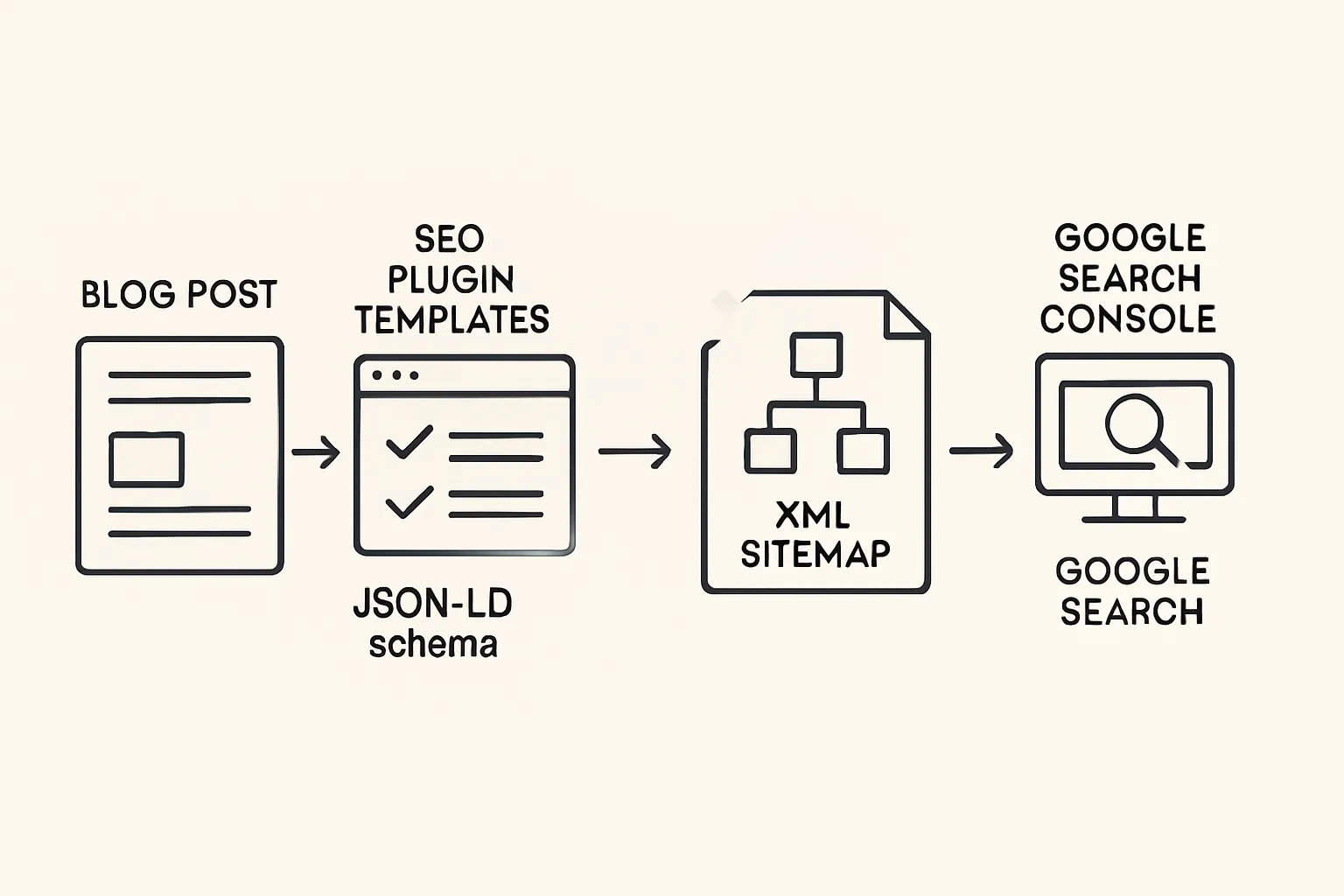
Configure basics
Set search-friendly permalinks
Settings → Permalinks → Post name. Keep URLs short and descriptive.
Enable HTTPS and preferred domain
Force HTTPS, set canonical host (www vs non-www) at your host or CDN; update WordPress Address and Site Address.
Choose a lightweight, fast theme
Use performance-first themes (e.g., GeneratePress, Astra, Block themes). Avoid bundled sliders and heavy builders.
Titles & meta (Yoast/Rank Math)
Global templates + per-post overrides
Set title/meta templates that front-load intent; override on key pages and posts.
Prevent duplicate titles; tidy archives
Disable automatic title duplication in archives; write unique archives or noindex them if thin.
Canonicals & indexation
Auto-canonical on posts/pages
Let the SEO plugin set self-referencing canonicals for single posts and pages.
Noindex thin/tag archives if needed
Apply noindex to tag archives, date archives, search results, or pagination pages that shouldn’t rank.
Schema markup
Article, Organization, Breadcrumb, ImageObject
Enable in your SEO plugin; set Organization/Logo/Social profiles globally.
Validate with Rich Results Test
Test representative URLs to confirm Article and Breadcrumb are valid.
json { "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Article", "headline": "{{post_title}}", "datePublished": "{{date_published}}", "dateModified": "{{date_modified}}", "author": { "@type": "Person", "name": "{{author_name}}" }, "image": [ "{{featured_image_url}}" ], "mainEntityOfPage": { "@type": "WebPage", "@id": "{{canonical_url}}" }, "publisher": { "@type": "Organization", "name": "{{site_name}}", "logo": { "@type": "ImageObject", "url": "{{site_logo_url}}" } } }
### Sitemaps
- Auto-generate and submit in Search Console - Ensure /sitemap.xml (or plugin path) is reachable; submit in Google Search Console and monitor Coverage/Pages reports. ### Robots
- Allow important sections; block admin and feeds you don’t need indexed - Keep /wp-admin/ blocked; don’t block /wp-includes/ assets. Avoid disallowing CSS/JS. Noindex low-value feeds or internal utility pages via meta robots. ### Media performance
- WebP/AVIF, lazy-load, responsive sizes, CDN - Serve next-gen formats, ensure srcset/sizes, enable native lazy loading, and use a CDN. Compress aggressively while retaining clarity. ### Pagination & categories
- Category strategy; avoid thin paginated pages - Use descriptive category names and intro copy. Link to pillars from category pages. Consider noindex for deep paginated pages with little unique value. ### Final checks
- Lighthouse/PSI, Mobile-Friendly, snippet preview - Run PageSpeed Insights/Lighthouse for Core Web Vitals. - Verify mobile usability. - Use your SEO plugin’s snippet preview to check title/description truncation and keyword visibility. ### Optional: do it in one click with BlogBowl (automated titles, schema, images, internal links)
- BlogBowl auto-publishes SEO-optimized posts with titles/meta, JSON-LD schema, optimized images, internal linking, sitemaps, and indexation-ready settings - ideal if you want results without manual configuration. ## Blogger (Blogspot): meta tags and technical SEO setup 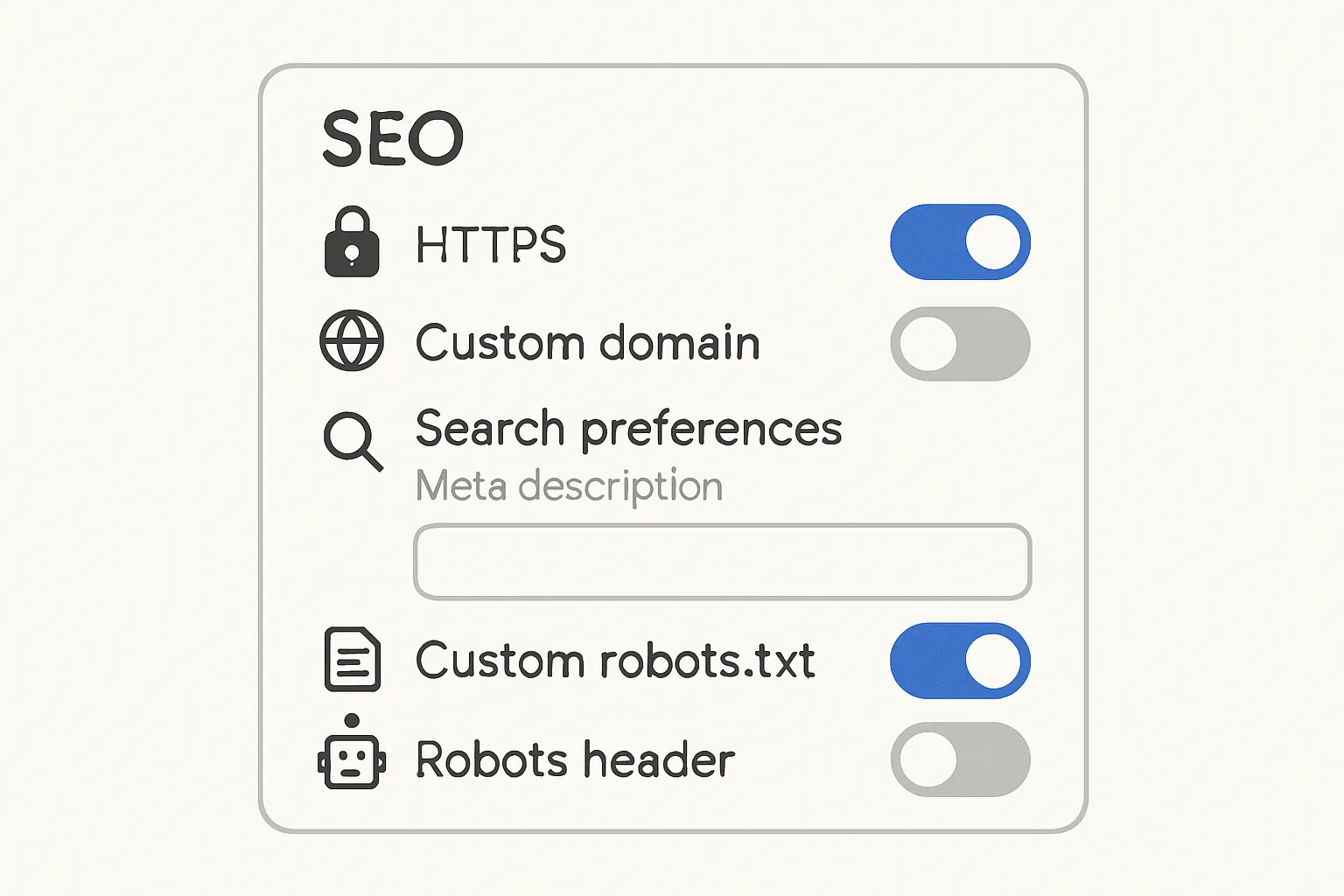 ### Turn on essentials
- HTTPS + custom domain - In Settings → HTTPS, enable “HTTPS Availability” and “HTTPS Redirect.” - Connect a custom domain for trust, cleaner URLs, and better canonical signals.
- Search preferences: enable meta description - Settings → Meta tags → Enable search description, then write a concise site-wide description. ### Titles & descriptions
- Write per-post descriptions; keep concise - In the Post editor → Search description: write a ~150–160 character summary with a clear benefit and intent. ### Canonicalization
- Ensure rel=canonical points to the post URL (built-in, verify) - Blogger outputs canonicals for posts by default; view source to confirm it points to the clean post URL (no parameters). ### Custom robots.txt and robots headers
- Allow posts; block search pages/labels if thin - Settings → Crawlers and indexing → Enable custom robots.txt and custom robots header tags. - Block /search (dynamic label/search pages) from indexing; keep posts and pages indexable. ### Schema
- Add Article JSON-LD to theme (before </head>) - Theme → Edit HTML. Paste a minimal Article schema that references your post title, author, dates, image, and canonical URL. json
{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Article", "headline": "{{post.title}}", "author": { "@type": "Person", "name": "{{post.author}}" }, "datePublished": "{{post.publishedDate}}", "dateModified": "{{post.modifiedDate}}", "image": ["{{post.featuredImageUrl}}"], "mainEntityOfPage": { "@type": "WebPage", "@id": "{{post.canonicalUrl}}" }, "publisher": { "@type": "Organization", "name": "{{site.name}}", "logo": { "@type": "ImageObject", "url": "{{site.logoUrl}}" } }
}
Sitemaps
Use default sitemap: /sitemap.xml or /atom.xml?redirect=false&start-index=1&max-results=500
Add multiple Atom sitemap lines if you have more than 500 posts.
Submit to Search Console
In Google Search Console → Sitemaps, submit sitemap.xml (and additional Atom feeds if needed).
Images & speed
Compress, WebP where possible, describe alt text
Upload optimized images; use WebP if available. Add descriptive alt text and keep file sizes small for faster loads.
# Sample robots.txt for Blogger
User-agent: *
Disallow: /search
Allow: / Sitemap: https://{{your-domain}}/sitemap.xml
# If using Atom feed pagination for large blogs, you can also submit:
# https://{{your-domain}}/atom.xml?redirect=false&start-index=1&max-results=500
Google Sites: what you can and can’t control (and how to still win)
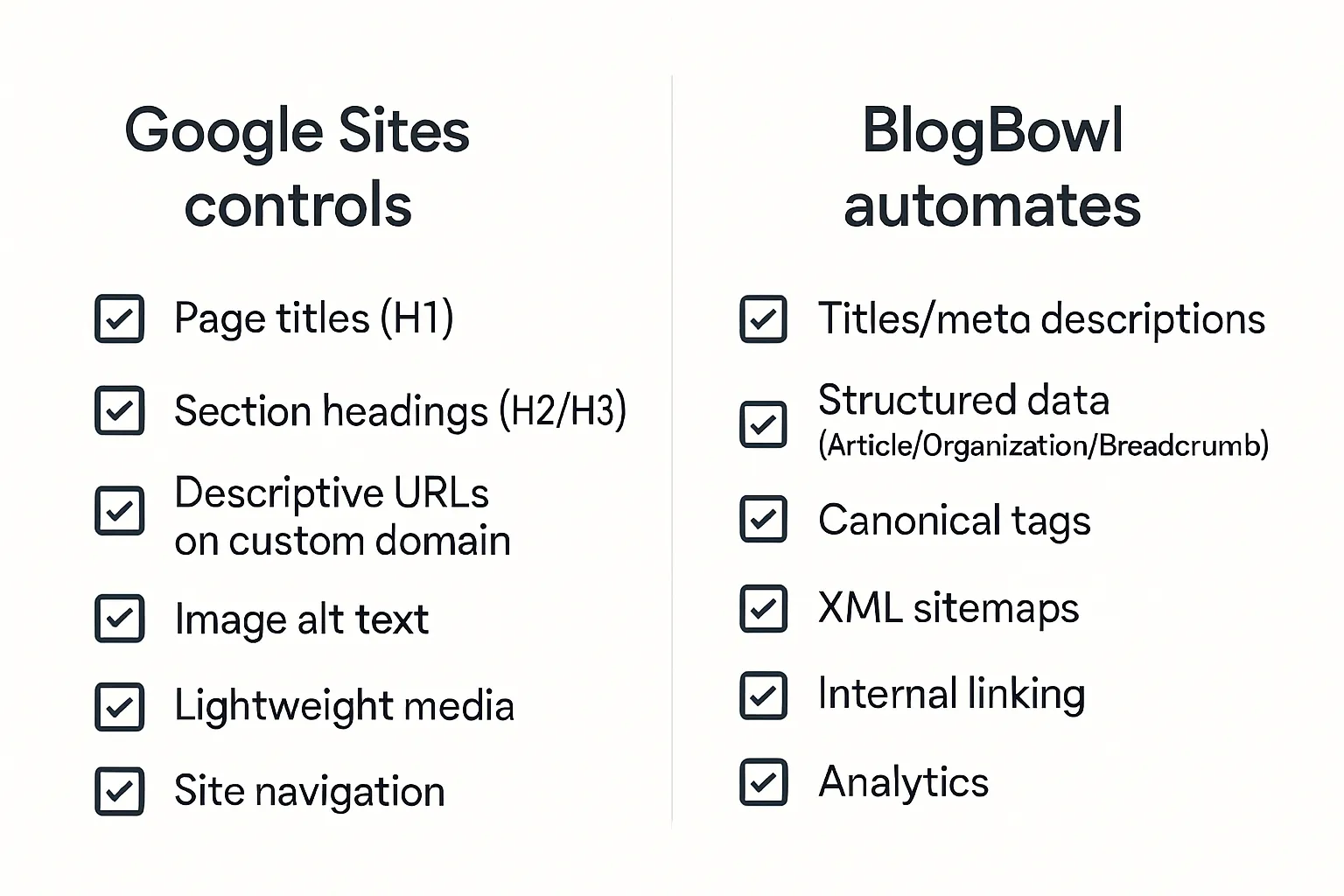
Reality check: limited head access and structured data
Google Sites is purpose-built for simplicity - great for speed, not so great for granular SEO. You don’t get direct head edits for advanced meta tags or JSON-LD, and manual sitemap controls are limited. The upside: clean HTML, fast loads, and fewer ways to break things. The playbook here is to maximize what you can control and use smart workarounds for the rest.
What you can control
Clear page titles (H1) and section headings (H2/H3)
Use intent-driven, scannable headings. Front-load key phrases naturally.
Descriptive URLs on custom domain
Map your Google Site to a custom domain for memorable, trustworthy URLs and clearer canonical signals.
Alt text for images; lightweight media
Add descriptive alt text and keep images small, using compressed formats where possible to maintain speed.
Indexation & discovery
Verify in Search Console; submit site property
Verify your custom domain or domain property so you can monitor coverage, page indexing, and enhancements.
Link from your main domain navigation for crawl discovery
Add prominent links to and from your main site. Cross-linking improves discovery and passes context.
Sitemaps & schema workarounds
Sites lacks manual sitemaps/structured data; rely on internal linking, navigation, and external references
Use clear menus, footer links, and hub pages to expose all content.
Publish supporting content on platforms you control (e.g., your main site, documentation, or social profiles) that link into your Google Site to speed discovery and provide corroboration.
When to switch or augment with BlogBowl
Use BlogBowl for the blog (full meta/schema/sitemaps) and embed/links from Google Sites
Keep Google Sites for pages and lightweight microsites. Run your blog on BlogBowl to get automated titles/meta, schema, canonical tags, XML sitemaps, internal linking, newsletter, and analytics.
Link to BlogBowl posts from your Google Site navigation and key pages. This hybrid setup preserves simplicity while unlocking complete SEO control for your content engine.
Canonicalization, duplication, and pagination
Canonicalization keeps your authority on the right URL. Done poorly, duplicates split link equity and confuse crawlers; done well, they consolidate signals and protect rankings.
Common duplication sources
HTTP/HTTPS, www/non-www, and trailing slashes
Force a single canonical host and slash style via 301s at the server/CDN.
UTM parameters and session IDs
Marketing links often add ?utm_source=… or ?ref=…. Canonical back to the clean URL so signals consolidate.
Tag/category archives vs single posts
Archives can mirror post excerpts or full content. If thin or duplicative, consider noindex and use excerpts only.
Printer-friendly or AMP variants
Printer/AMP versions must canonical back to the primary article URL.
Staging/preview URLs, case/uppercase variants, and parameters like ?replytocom
Block staging with auth, normalize case, canonicalize parameterized pages.
Implementing rel=canonical correctly
Point to the preferred URL; avoid canonical loops and contradictions
The preferred page should self-canonical.
Consolidated pages must canonical to the preferred page (not to themselves).
Avoid redirecting to a URL that then canonicalizes somewhere else.
Align internal links and sitemaps with the canonical
Link to the preferred URL internally; list only canonical URLs in XML sitemaps.
Don’t use canonicals to mask fundamentally different content
Canonical is a hint for near-duplicates, not for merging unrelated pages.
Syndication and republishing
Use cross-domain canonicals when your article appears elsewhere
Ask partners to add on the republished version.
Publish on your site first; keep titles similar and include an attribution note to reduce ambiguity.
Pagination
Consolidate signals to page 1 via internal links; noindex thin pages when necessary
Since rel="prev/next" is no longer used by Google, keep each paginated URL self-canonical.
Link prominently to page 1 (and key posts) from paginated pages to concentrate authority.
If deep paginated pages are thin or low-value, consider noindex (but ensure users can still navigate).
Prefer “view all” pages when performance allows.
Content hygiene
De-duplicate near-identical posts; merge and redirect
Choose the strongest URL, consolidate content, 301 the rest, and update internal links.
Audit parameters and archives quarterly to catch new duplicates early.
Robots, sitemaps, and index control (platform matrix)
Robots, sitemaps, and index settings control what search engines can access, how they discover URLs, and which pages are eligible to rank. Use the matrix and templates below to configure each platform safely.
Robots.txt best practices by platform
WordPress: block /wp-admin/, allow core assets
Keep /wp-admin/ disallowed; allow admin-ajax.php. Don’t block CSS/JS needed to render pages.
Blogger: block /search, allow posts
Disallow label/search result pages if thin. Keep post URLs crawlable.
Google Sites: limited control; rely on Search Console settings
No direct robots.txt editing; use clean navigation, and manage indexing in Search Console where possible.
XML sitemaps
WordPress SEO plugin vs native
WordPress 5.5+ includes a native sitemap, but SEO plugins (Yoast/Rank Math) provide richer control. Submit only one sitemap index if using a plugin.
Blogger auto-sitemap endpoints
Use /sitemap.xml or paginate Atom feeds for large sites: /atom.xml?redirect=false&start-index=1&max-results=500
Google Sites alternatives
Limited sitemap control; rely on clear internal linking and submit the property in Search Console for discovery.
"Sitemaps are not mandatory for your website to appear in Google Search results; however, they can significantly aid Google in discovering and understanding your site's content." - Source
Noindex safely
When to noindex thin archives, pagination, test pages
Noindex tag/date/search archives if thin or duplicative.
Keep core category pages indexable when they add value (intro copy, curated links).
Noindex staging/test pages; block with authentication when possible.
Submit and monitor
Search Console: Sitemaps and Page indexing reports
Submit your primary sitemap index.
Check Page indexing to resolve “Crawled – currently not indexed,” “Alternate page with proper canonical tag,” and soft 404s.
Revalidate after fixes and watch trend lines over time.
Platform feature matrix
Platform | robots.txt control | Sitemap availability | Per-page noindex | Canonical control | Schema flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
WordPress | Yes (file or plugin) | Yes (native or plugin index) | Yes (SEO plugins) | Yes (plugins/self-canonical) | High (plugins/custom JSON-LD) |
Blogger (Blogspot) | Yes (custom robots.txt) | Yes (/sitemap.xml + Atom feeds) | Partial (robots headers per post) | Partial (built-in; limited override) | Partial (theme edits for JSON-LD) |
Google Sites | Partial/No (no direct edit) | Partial (limited; rely on GSC) | No (no per-page meta robots) | No (no custom canonicals) | Low (no custom head/JSON-LD) |
Robots.txt templates
txt
WordPress robots.txt
User-agent: * Disallow: /wp-admin/ Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php
Don’t block CSS/JS needed for rendering.
If using an SEO plugin, prefer its sitemap index:
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap_index.xml
Otherwise, native WP 5.5+:
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
```txt
# Blogger (Blogspot) robots.txt
User-agent: *
Disallow: /search
Allow: / # Primary auto-sitemap:
Sitemap: https://your-domain.com/sitemap.xml
# For large blogs, also submit Atom feeds (in GSC, not necessarily here):
# https://your-domain.com/atom.xml?redirect=false&start-index=1&max-results=500
# https://your-domain.com/atom.xml?redirect=false&start-index=501&max-results=500
Use this matrix and the templates to set precise crawl controls, keep your XML sitemaps clean, and ensure only your best URLs are indexed - foundational moves for reliable SEO for blog posts on WordPress, “seo for blogger blogspot,” and simple Google Sites setups.
Speed and Core Web Vitals for blogs
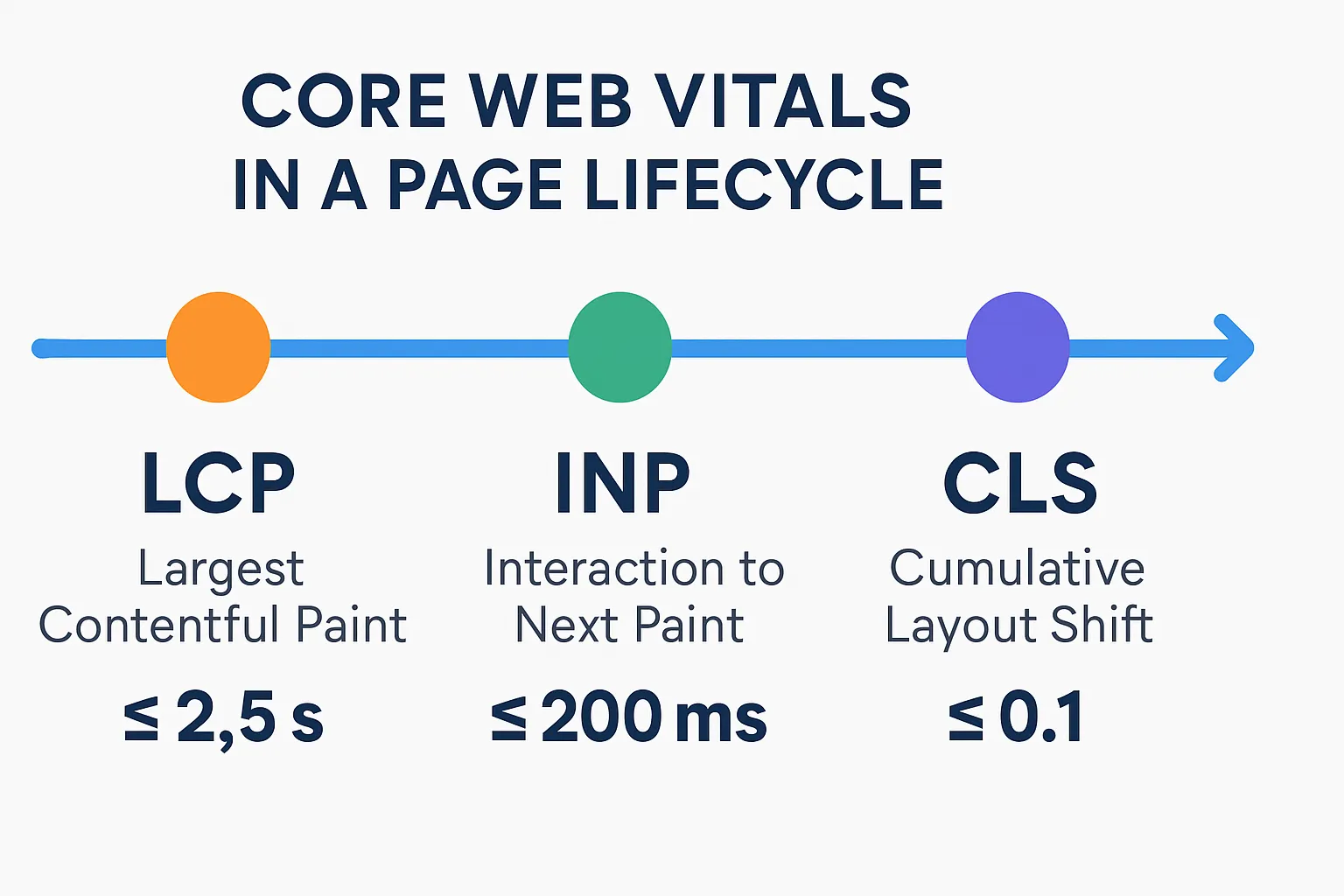
"Good thresholds: LCP ≤ 2.5s, INP ≤ 200ms, CLS ≤ 0.1 (measured at the 75th percentile across devices)." - Source
Targets that matter in 2025: LCP, INP (replacing FID), and CLS
LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): Time to render the main content. Target ≤ 2.5s.
INP (Interaction to Next Paint): Overall interaction latency replacing FID. Target ≤ 200ms.
CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): Visual stability. Target ≤ 0.1.
Quick wins
Compress images (WebP/AVIF), responsive sizes, lazyload
Serve next-gen formats, generate srcset/sizes, and use native loading="lazy" for below-the-fold media.
Defer non-critical JS; limit heavy plugins/widgets
Defer or async third-party scripts; audit and remove unused libraries.
Preload key fonts; reduce render-blocking CSS
Preload primary text fonts; inline critical CSS and defer the rest.
Platform-specific tips
WordPress: caching, CDN, critical CSS
Use page caching and object caching; deliver via CDN; generate critical CSS; minimize plugin count and avoid heavy builders.
Blogger: lean templates, minimal third-party scripts
Choose lightweight themes; keep widgets to essentials; compress images before upload.
Google Sites: keep pages light, optimize media
Limit embedded widgets; compress imagery and video; split long pages into logical sections.
Measure and iterate
Lighthouse, PageSpeed Insights, Chrome UX Report, Search Console CWV report
Validate lab and field data. Fix regressions early and re-test after each change.
Pre-publish QA and ongoing monitoring
Per-post preflight
Title tests (intent-first), meta description, slug hygiene
Front-load the primary intent; keep titles ≈55–60 chars; use clean, hyphenated slugs.
Canonical correct; robots meta set; OG/Twitter present
Self-canonical on main URL; use index,follow unless intentionally blocking; ensure social cards render.
Internal links added; external references cited
Link to pillar pages and related posts; cite authoritative sources where relevant.
Image alt text, compression, dimensions
Descriptive alt text; WebP/AVIF where possible; use responsive sizes and lazy loading.
Validation tools
URL Inspection, Rich Results Test, social debuggers
Confirm indexability, canonical, schema validity, and social previews before publishing.
Post-publish
Submit URL in Search Console; check coverage
Request indexing and review Page indexing status.
Track impressions, CTR, average position; iterate titles
Revisit titles/meta after 2–4 weeks to lift CTR while preserving intent.
Quarterly hygiene
Fix broken links; refresh evergreen posts; redirect retired URLs
Update facts, screenshots, and examples; consolidate overlapping content and 301 the weaker URLs.
Automate the boring parts
Use BlogBowl to auto-insert schema, internal links, media, and refreshes
BlogBowl handles titles/meta, JSON-LD, internal linking, and image optimization at scale, so you can focus on new content.
Per-post QA checklist (quick reference)
Item | Why it matters | Tool/Where to check |
|---|---|---|
Title tag (intent-first) | Drives clicks and communicates relevance | SEO plugin snippet preview; live SERP preview tools |
Meta description | Improves CTR with a clear benefit + CTA | SEO plugin snippet preview |
Slug hygiene | Short, readable URLs aid sharing and clarity | CMS editor (Permalink/Slug field) |
Canonical URL | Consolidates signals to the preferred URL | View Source; URL Inspection → Inspect page |
Robots meta | Ensures page is indexable when intended | View Source; URL Inspection |
Open Graph/Twitter tags | Better social previews and secondary traffic | Facebook Sharing Debugger; X Card Validator |
Internal links added | Boosts crawl depth and topical authority | On-page review; internal link suggestions |
External references cited | Enhances credibility and context | On-page review |
Image alt/compression/dimensions | Accessibility + LCP improvements | Media library; Lighthouse/PSI waterfall |
Schema (Article/Breadcrumb) | Eligibility for rich results | Rich Results Test; URL Inspection → Enhancements |
Indexable and not blocked | Prevents accidental exclusion | URL Inspection → Page indexing |
Included in sitemap | Faster discovery and easier monitoring | /sitemap.xml; Search Console → Sitemaps |
Mobile rendering | Majority of traffic; mobile-first indexing | Mobile-friendly test; device preview |
Core Web Vitals quick check | Catch LCP/INP/CLS regressions | Lighthouse/PSI; Search Console → CWV report |
Snippet appearance | Avoids truncation; highlights key value | SEO plugin preview; SERP emulator |
404s/redirects sanity | Clean navigation; no soft 404s | Screaming Frog or site crawl; manual spot-check |
Ads/widgets weight | Prevents CLS/INP issues | Lighthouse/PSI diagnostics |
Post-publish indexing | Confirms discovery and eligibility | Search Console → Request Indexing; Page indexing |
Performance tracking | Iterate titles/meta and internal links | Search Console → Performance (queries/pages) |
Change log | Document edits for faster QA later | Editorial notes; CMS revisions |
Conclusion: grow faster with BlogBowl’s automated blog SEO
Recap: meta tags + technical SEO = crawlability, relevance, and rich results
Strong blog meta tags and a clean technical setup do the heavy lifting for discoverability:
Crawlability: Robots, sitemaps, and index controls ensure the right URLs get found and indexed.
Relevance: Title tags, meta descriptions, and canonicals align your content to search intent and consolidate authority.
Rich results: Valid schema (Article, Organization, Breadcrumb, ImageObject) helps Google and AI systems understand your content and display it more prominently.
Together, these turn good “seo for blog posts” into durable visibility - higher CTRs, fewer duplicate-URL headaches, and content that scales.
Why BlogBowl: automated titles/descriptions, schema, sitemaps, internal links, AI articles, and analytics
BlogBowl removes the tedious parts of blog content SEO so you can focus on strategy and storytelling:
Automated meta: High-quality title tags and meta descriptions that match user intent
Smart canonicals and index controls: Consolidate duplicates and avoid accidental noindex
Built-in schema: Article, Organization, Breadcrumb, ImageObject - validated out of the box
Sitemaps + Search Console–ready: Always-fresh XML sitemaps, optimized for discovery
Internal linking automation: Contextual links that reinforce topical authority
AI-powered content: Daily SEO-optimized articles, on-brand images, and embedded videos
Performance-first templates: Fast, mobile-friendly themes that pass Core Web Vitals
Integrated analytics and newsletter: Track what performs and grow your audience in one place
Multi-blog and multi-author: Scale your “best SEO blog” operations without extra overhead
Next steps: start a free trial at blogbowl.io and launch an SEO-optimized blog in under 60 seconds
Ready to turn this checklist into results without manual grind? Launch a BlogBowl blog, connect your domain, and publish with automated SEO baked in.
Get started: https://www.blogbowl.io
Build momentum fast - titles, descriptions, schema, sitemaps, internal links, and analytics are handled for you. You focus on the ideas; BlogBowl handles the ranking signals.

-cover.webp)
